
What Is a Fast Casual Restaurant? | Examples from Around The World
The fast casual restaurant model has been gaining momentum around the world as consumers increasingly seek convenient yet high-quality dining experiences. Positioned between fast food and casual dining, fast casual restaurants offer a balance of quick service and healthier, fresher options, appealing to a wide range of diners. With the growing emphasis on transparency, customization, and sustainability, the fast casual sector has become a dominant force in the global food industry.
This type of dining experience is particularly popular among millennials and Gen Z, who prioritize convenience, quality, and the ability to personalize their meals. The rise of health-conscious eating and the demand for more sustainable food choices have only fueled the popularity of these establishments. Fast casual restaurants not only deliver quick service but also provide an inviting atmosphere where customers can enjoy made-to-order meals, often featuring premium ingredients.
From Chipotle in the U.S. to LEON in Europe, fast casual concepts have evolved to meet diverse cultural and culinary expectations. This article will explore the core elements of fast casual dining, examine global examples, and offer insights for those looking to enter this rapidly growing market.
Would you like to listen our deep-dive conversation about this article?
Defining the Fast Casual Restaurant Concept
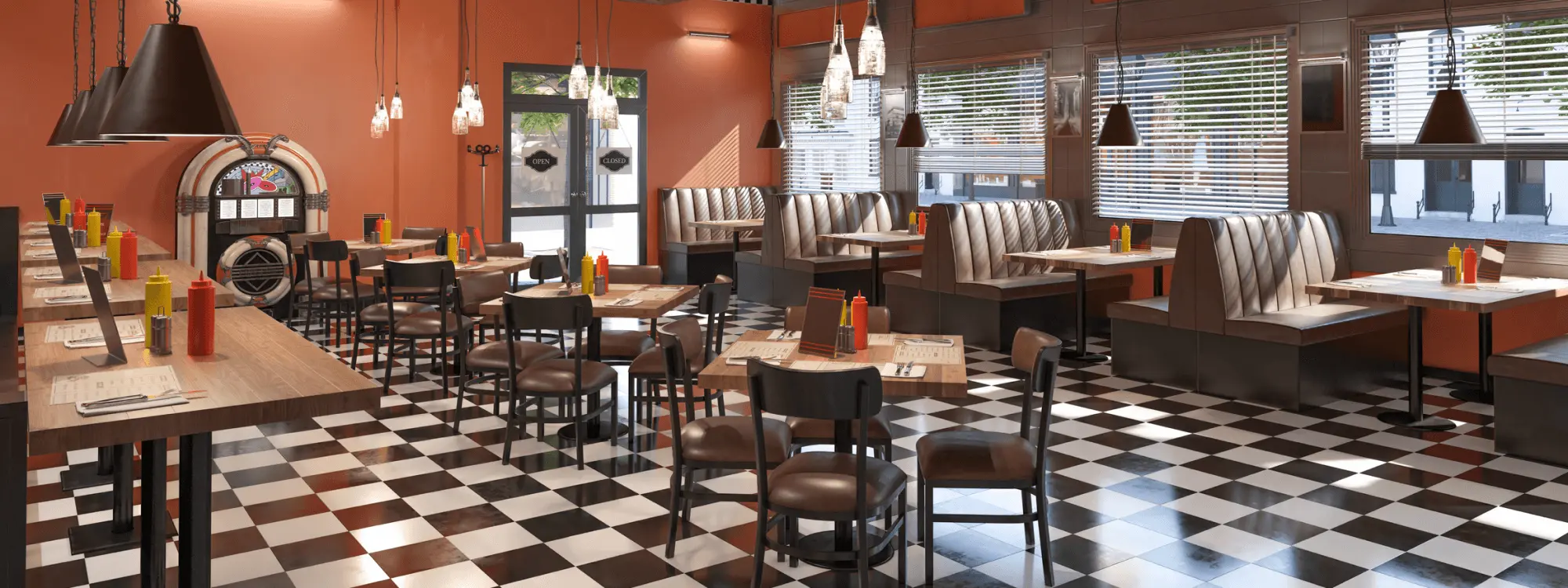
Fast casual restaurants have carved out a distinct space in the dining world, offering a unique blend of convenience, quality, and experience. They provide an option that bridges the gap between fast food’s speed and casual dining’s attention to fresh ingredients and atmosphere. In this section, we’ll break down what truly defines a fast casual restaurant, its distinguishing characteristics, and why it’s becoming such a popular choice for today’s diners.
What is a Fast Casual Restaurant?
A fast casual restaurant is a dining establishment that blends the convenience of fast food with the quality of casual dining. These restaurants usually:
- Offer counter service with no full table service.
- Provide made-to-order meals using fresh ingredients.
- Feature a more upscale ambiance compared to traditional fast food.
- Price meals slightly higher than fast food but lower than full-service restaurants.
Fast casual focuses on delivering higher quality meals without compromising on speed or efficiency, positioning itself as an attractive option for both time-conscious and health-conscious consumers.
How Fast Casual Differs from Fast Food and Full Service
Understanding how fast casual differs from other dining formats is key to defining its appeal.
- Fast food:
- Focuses on speed, often using pre-prepared ingredients.
- Typically features a drive-thru and lower-cost meals.
- Minimal focus on ambiance or in-restaurant experience.
- Full service/casual dining:
- Involves table service and a more extensive menu.
- Meals are prepared and plated in the kitchen, often leading to longer wait times.
- Higher meal costs, with tips generally expected.
Fast casual finds the sweet spot, offering fresh, high-quality food with faster service than traditional casual dining.
Key Features of a Fast Casual Dining Experience
Fast casual restaurants are distinguished by several core features:
- Made-to-order meals: Customers can customize their dishes, selecting from a variety of fresh, healthy ingredients.
- No table service: Orders are typically placed at a counter, though many fast casual restaurants provide a more upscale, comfortable seating area for diners.
- Emphasis on quality:
- Ingredients are often locally sourced, organic, or sustainably produced.
- Meals focus on being healthier and more artisanal compared to traditional fast food.
- Flexible dining:
- Customers can choose to dine in, take their meals to-go, or order online for delivery.
Fast casual dining revolves around offering a better experience without the wait, combining convenience with high food standards.
Evolution and Growth of Fast Casual Restaurants
Fast casual restaurants have emerged as a significant force in the global dining landscape over the last few decades. Their evolution is closely tied to changing consumer preferences, health-conscious trends, and the desire for higher quality dining experiences at a reasonable price. In this section, we will trace the origins of the fast casual movement, discuss its rise in popularity, and explore the key trends driving its continued growth.
Origins of the Fast Casual Movement
The concept of fast casual dining began to take shape in the 1990s, particularly in the United States. Some of the first fast casual pioneers include:
- Panera Bread (originally St. Louis Bread Co.): Focused on freshly baked goods and quality ingredients, it set the foundation for what fast casual could become.
- Chipotle Mexican Grill: Redefined the idea of fast food by emphasizing transparency in sourcing and customizable meals made with fresh, organic ingredients.
These early adopters sought to break away from the stereotypical fast food model by offering better quality and a more enjoyable dining atmosphere.
The Rise of Health-Conscious and Customizable Menus
One of the core factors behind the growth of fast casual dining is the increasing focus on health and wellness. Consumers are more informed and selective about what they eat, with an emphasis on:
- Healthier options:
- Fresh produce, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Gluten-free, vegan, and low-carb menu choices.
- Customization:
- Ability to build a meal that suits individual dietary needs and preferences.
- Interactive ordering, where customers can see and choose exactly what goes into their meal.
As people became more health-conscious, fast casual restaurants responded with offerings that catered to dietary preferences, food allergies, and ingredient transparency.
Why Fast Casual Appeals to Millennials and Gen Z
Millennials and Gen Z are driving much of the demand for fast casual dining, largely because of their unique preferences:
- Convenience: These generations value quick, efficient service without compromising on quality.
- Personalization: They seek options that allow them to customize their meals to suit their tastes or dietary restrictions.
- Social responsibility: Many fast casual brands emphasize sustainability, ethical sourcing, and community impact—values that resonate strongly with younger diners.
These factors have made fast casual dining a staple for millennials and Gen Z, leading to its rapid expansion across urban and suburban areas.
Trends Driving the Popularity of Fast Casual in 2024
Several trends are pushing the continued growth of fast casual dining:
- Sustainability: An increasing number of restaurants are prioritizing eco-friendly practices, such as:
- Sourcing local and organic ingredients.
- Reducing food waste and using biodegradable packaging.
- Technology integration:
- Online ordering and delivery services have exploded in popularity.
- Contactless payments and mobile apps for customized orders are now commonplace.
- Health-focused innovations:
- Plant-based menus and alternative proteins (e.g., Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods).
- Nutritional transparency and calorie counts displayed on menus.
Fast casual restaurants are well-positioned to evolve alongside these trends, continuing to cater to the growing demand for convenient, high-quality, and socially responsible dining options.
Fast Casual Restaurant Models from Around the World
The fast casual dining concept has taken root across the globe, with regional variations reflecting local tastes, ingredients, and dining preferences. From North America to Asia and beyond, fast casual restaurants have adapted to different cultures while maintaining their core principle of offering quality food quickly. In this section, we’ll explore successful fast casual models from different parts of the world, highlighting how each brand reflects the unique characteristics of its region.
North America: Chipotle, Panera Bread, Sweetgreen
North America is the birthplace of many fast casual pioneers, with notable examples including:
- Chipotle Mexican Grill:
- Specializes in customizable burritos, bowls, and tacos.
- Known for its commitment to sustainably sourced ingredients and transparent supply chain.
- Panera Bread:
- Offers freshly baked bread, soups, salads, and sandwiches in a cozy, café-style setting.
- One of the early brands to promote nutritional transparency and clean ingredients.
- Sweetgreen:
- A salad-focused chain that emphasizes locally sourced, organic produce.
- Known for its seasonal menus and commitment to sustainability.
These brands reflect the American consumer’s desire for fresh, healthy, and customizable meals with a focus on quality and ethical sourcing.
Europe: LEON, Vapiano, Pret A Manger
Europe has embraced fast casual dining with a mix of local and international influences:
- LEON (UK):
- Focuses on “natural fast food,” offering healthy, Mediterranean-inspired dishes.
- Known for its emphasis on clean eating, with a menu that caters to gluten-free and vegan customers.
- Vapiano (Germany):
- Blends fast casual with an Italian twist, offering pasta, pizza, and salads made fresh to order.
- Customers can watch their meals being prepared in an open kitchen, enhancing the dining experience.
- Pret A Manger (UK):
- Known for freshly made sandwiches, wraps, and salads using organic and sustainable ingredients.
- Aims to provide quick meals for on-the-go customers, with an emphasis on freshness and quality.
These European models highlight the region’s focus on healthy eating, sustainability, and offering a more personalized dining experience.
Asia: Wagas, Element Fresh, Gyu-Kaku
Asia’s fast casual scene is growing rapidly, with many local and international brands making an impact:
- Wagas (China):
- A Shanghai-based chain offering fresh salads, wraps, and pasta with a Western influence.
- Known for its focus on health-conscious meals and minimalist, modern dining spaces.
- Element Fresh (China):
- A pioneer in offering healthy and fresh meals, including smoothies, sandwiches, and salads.
- Appeals to urban professionals seeking nutritious food in a fast-paced environment.
- Gyu-Kaku (Japan):
- Specializes in yakiniku (grilled meat), allowing diners to cook their food at the table.
- Combines the social aspect of communal dining with the convenience of fast casual service.
Asia’s fast casual concepts often emphasize health, customization, and efficiency, catering to the demands of urban diners who value fresh and high-quality ingredients.
Middle East: Operation Falafel, Zaatar W Zeit
The Middle East has seen the rise of fast casual brands that blend traditional flavors with modern dining trends:
- Operation Falafel (UAE):
- Offers a modern take on traditional Middle Eastern street food, including falafel, shawarma, and mezze.
- Combines authentic flavors with a fast casual service model in a contemporary setting.
- Zaatar W Zeit (Lebanon):
- Known for its manoushe (Lebanese flatbread) and wraps, with a focus on fresh ingredients and quick service.
- Appeals to both traditional tastes and modern dining preferences, offering a mix of classic and innovative dishes.
These Middle Eastern brands bring a unique fusion of tradition and modernity to the fast casual scene, focusing on authentic flavors delivered quickly.
South America: Poke Me, Tostado Café Club
In South America, fast casual dining has adapted to local tastes while incorporating global trends:
- Poke Me (Brazil):
- Offers Hawaiian-inspired poke bowls with customizable ingredients, blending local flavors with international trends.
- Emphasizes fresh, raw ingredients like fish, vegetables, and grains, catering to health-conscious diners.
- Tostado Café Club (Argentina):
- Specializes in coffee and toast-based dishes, offering quick, fresh options for breakfast and lunch.
- Combines café culture with a fast casual approach, making it a popular choice for urban professionals.
Fast casual in South America often focuses on fresh, locally sourced ingredients and an informal yet comfortable dining experience.
Africa: Nando’s, RocoMamas
Africa’s fast casual scene is highlighted by brands that have gained international recognition:
- Nando’s (South Africa):
- Known for its flame-grilled peri-peri chicken, combining fast casual service with bold, spicy flavors.
- The brand has expanded globally while maintaining its South African roots.
- RocoMamas (South Africa):
- Specializes in burgers, ribs, and wings, with a focus on a “smash burger” concept where patties are freshly prepared.
- Combines a casual, vibrant atmosphere with quality ingredients and quick service.
African fast casual brands emphasize bold, flavorful dishes with a focus on fresh preparation and quick delivery, appealing to both local and international customers.
Fast Casual vs. Other Restaurant Types
Understanding how fast casual restaurants differ from other dining formats is crucial for both consumers and aspiring restaurant owners. While fast casual shares some similarities with fast food, casual dining, and quick service, it stands out for its unique blend of quality, speed, and customer experience. In this section, we will break down the differences between fast casual and other popular restaurant types to highlight what makes this model so appealing.
Fast Casual vs. Fast Food: What’s the Difference?
Fast casual and fast food might seem similar at first glance, but they cater to very different dining preferences. Here’s how they differ:
- Quality of ingredients:
- Fast casual: Focuses on fresher, often locally sourced or organic ingredients.
- Fast food: Primarily uses pre-packaged or frozen ingredients to minimize costs and preparation time.
- Customization:
- Fast casual: Offers more menu customization, allowing customers to personalize their meals (e.g., build-your-own bowls or salads).
- Fast food: Limited customization options; meals are usually pre-set with specific combinations.
- Dining atmosphere:
- Fast casual: More upscale interiors with a focus on ambiance and comfort, often designed to encourage dining in.
- Fast food: Basic, functional spaces aimed at fast turnover, often with a focus on takeout or drive-thru.
- Pricing:
- Fast casual: Typically priced higher due to better ingredients and a more premium experience.
- Fast food: Cheaper, with meals designed to be affordable and quick.
While fast food prioritizes speed and low cost, fast casual aims to elevate the dining experience without sacrificing convenience.
Fast Casual vs. Casual Dining: Key Contrasts
Fast casual lies between fast food and casual dining, combining the benefits of both models:
- Service style:
- Fast casual: Counter service, where customers order at a counter and either wait for their food or receive it directly from staff. No table service.
- Casual dining: Full-service experience with servers who take orders at the table and deliver meals.
- Meal preparation time:
- Fast casual: Meals are prepared quickly, often within 10-15 minutes.
- Casual dining: Longer wait times, with meals generally taking 20-30 minutes or more.
- Price range:
- Fast casual: More affordable than casual dining, with average meal prices ranging from $8 to $15.
- Casual dining: Higher-priced, with meals typically costing $15 to $30, including gratuity.
- Menu options:
- Fast casual: Streamlined menu focusing on fresh, customizable, and often healthier options.
- Casual dining: Larger, more diverse menus with a wider range of appetizers, entrées, and desserts.
Fast casual restaurants offer many of the benefits of casual dining, such as high-quality food, but with quicker service and a lower price point.
Fast Casual vs. Quick Service: Understanding the Overlap
Fast casual and quick service are sometimes confused because they both emphasize speed and convenience. However, there are critical distinctions:
- Level of food quality:
- Fast casual: Prioritizes fresh, minimally processed ingredients, often prepared in open kitchens where customers can see the cooking process.
- Quick service: Similar to fast food, it uses more processed or pre-prepared ingredients to ensure speed.
- Dining experience:
- Fast casual: Typically has a more welcoming atmosphere, with comfortable seating and a focus on enhancing the in-dining experience.
- Quick service: Primarily focused on takeout or drive-thru service, with minimal emphasis on dine-in ambiance.
- Customization and innovation:
- Fast casual: More room for innovation and customization, allowing diners to adjust ingredients and portion sizes.
- Quick service: Limited to standard menu items with fewer customization options.
Although quick service restaurants focus more on speed and efficiency, fast casual bridges the gap by offering a more refined experience while maintaining fast service.
Fast casual dining blends elements from these various models, offering flexibility, quality, and convenience without the limitations of fast food or the costs of casual dining. This makes it an increasingly popular option for diners seeking both speed and substance.
Benefits of Opening a Fast Casual Restaurant
Fast casual restaurants offer a variety of advantages for both customers and business owners. As the demand for quick, high-quality meals continues to grow, opening a fast casual restaurant presents a lucrative opportunity in the evolving dining landscape. In this section, we’ll explore the key benefits of starting a fast casual restaurant, focusing on factors like operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and the ability to adapt to market trends.
Lower Operational Costs Compared to Full-Service Restaurants
One of the most appealing aspects of a fast casual restaurant is the lower cost of operation compared to a full-service model. Key reasons include:
- Reduced labor costs:
- No need for a full waitstaff, which significantly lowers payroll expenses.
- Limited table service means fewer employees are required to handle customer orders and service.
- Smaller kitchen teams:
- Kitchens are typically more streamlined and efficient, with a focus on quick, made-to-order meals.
- This reduces the number of chefs and cooks needed compared to a full-service restaurant.
- Lower overhead costs:
- Fast casual spaces are often smaller and don’t require as much seating or elaborate décor, leading to reduced rent and utility expenses.
These reduced operational costs allow owners to invest in higher-quality ingredients or marketing without sacrificing profit margins.
Flexible Menu and Dining Formats for Market Trends
Fast casual restaurants are highly adaptable and can easily respond to changing consumer preferences. Benefits of this flexibility include:
- Evolving menus:
- Easy to introduce new dishes or seasonal items based on customer demand, such as plant-based options or gluten-free meals.
- Ability to cater to health trends like keto, vegan, or locally sourced ingredients.
- Multiple service options:
- Offer a variety of dining formats, including dine-in, takeout, and delivery.
- Many fast casual restaurants integrate digital ordering systems or apps to streamline the customer experience and expand their reach.
This flexibility allows fast casual restaurants to stay relevant in an ever-changing food landscape, adjusting to consumer tastes and trends.
Increased Customer Satisfaction Through Healthier Options
Today’s consumers are more health-conscious than ever, and fast casual restaurants are well-positioned to meet this demand. Benefits include:
- Health-focused menus:
- Fast casual restaurants often emphasize fresh, wholesome ingredients, such as organic produce, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Options like build-your-own bowls, salads, and wraps offer customization that fits various dietary needs (gluten-free, low-carb, vegan, etc.).
- Nutritional transparency:
- Many fast casual establishments prominently display calorie counts, nutritional information, and sourcing details.
- This transparency builds trust with customers and satisfies their desire for control over what they’re eating.
By offering healthier, customizable meals, fast casual restaurants can attract a loyal customer base that values quality, nutrition, and choice.
How Fast Casual Meets the Demand for Fast Yet Quality Dining
The fast casual model effectively caters to diners who seek both speed and quality, fulfilling a growing market need. Key advantages include:
- Faster service without compromising quality:
- Meals are typically ready within 10-15 minutes, providing the convenience of fast food but with better ingredients and preparation.
- Customers don’t have to wait for full table service but can still enjoy a higher caliber of food compared to typical quick-service establishments.
- Higher perceived value:
- Even though fast casual meals are priced higher than fast food, customers perceive them as a better value due to the focus on fresh ingredients and customizable options.
- The blend of speed, quality, and a more refined dining experience appeals to busy professionals, families, and health-conscious diners.
By bridging the gap between fast food and full-service dining, fast casual restaurants meet the growing demand for a better-quality, faster dining experience at an affordable price point.
These benefits highlight why fast casual dining has become one of the fastest-growing segments in the restaurant industry. By offering flexibility, operational efficiency, and healthier choices, fast casual concepts are well-positioned for continued success in an evolving marketplace.
Challenges Faced by Fast Casual Restaurants
While fast casual restaurants have grown in popularity, they are not without their challenges. Like any business model, fast casual dining comes with its own set of operational, financial, and competitive hurdles. In this section, we’ll discuss the key challenges that fast casual restaurant owners face and offer insights into how they can address these issues effectively.
Balancing Speed with Quality
One of the primary appeals of fast casual dining is the promise of high-quality food served quickly. However, maintaining this balance can be difficult:
- Operational pressure:
- Preparing fresh, made-to-order meals at a fast pace requires efficient kitchen operations.
- Mistakes or delays in preparation can lead to long wait times, undermining the “fast” aspect of the service.
- Staff training:
- Employees must be trained to work quickly while still ensuring the quality of each dish.
- Continuous staff development is necessary to avoid inconsistencies in meal preparation.
To succeed, fast casual restaurants need to invest in streamlined kitchen processes and ensure their staff can maintain the balance between speed and quality, even during peak times.
Managing Supply Chain for Fresh Ingredients
Fast casual restaurants typically emphasize fresh, high-quality ingredients, but sourcing these can present challenges:
- Supply chain complexity:
- Finding local or organic suppliers who can deliver consistently high-quality products can be difficult.
- Fluctuations in availability due to seasonality or logistics issues can impact the menu.
- Cost control:
- Fresh ingredients are often more expensive, leading to higher food costs.
- Managing the delicate balance between food quality and profitability can be a challenge, especially in times of rising costs.
To overcome these challenges, fast casual operators need to build strong relationships with reliable suppliers and have backup plans in place to deal with fluctuations in the supply chain.
The Struggle to Stand Out in a Saturated Market
As fast casual dining becomes increasingly popular, the market is becoming more crowded, making it harder for new restaurants to stand out:
- Brand differentiation:
- With so many similar concepts (e.g., build-your-own bowls, artisanal sandwiches), it’s challenging to offer something unique that captures customers’ attention.
- Restaurants need to clearly define their unique value proposition (UVP) to attract loyal customers.
- Competing with established brands:
- Established chains with larger marketing budgets and stronger brand recognition can overshadow smaller, independent fast casual restaurants.
- Independent operators may struggle to compete on advertising, pricing, or convenience.
To stand out in a competitive market, fast casual restaurants must focus on creating a distinctive brand, offering something unique—whether it’s a signature dish, an innovative dining experience, or a strong community presence.
How to Address Operational Challenges in a Fast Casual Model
Running a fast casual restaurant efficiently involves a variety of operational challenges:
- Peak hour traffic management:
- Many fast casual restaurants experience high traffic during lunch and dinner hours, which can strain kitchen staff and lead to longer wait times.
- Proper staffing and effective scheduling are critical to handle busy periods without sacrificing service quality.
- Consistency across locations:
- For fast casual chains or franchises, maintaining consistency across multiple locations can be difficult, especially as the business scales.
- Standardized operating procedures (SOPs), rigorous staff training, and regular audits are necessary to ensure the same level of quality and service in each location.
Addressing these operational challenges requires a proactive approach, focusing on systems and processes that ensure efficiency, consistency, and customer satisfaction.
How to Start Your Own Fast Casual Restaurant
Starting a fast casual restaurant can be a rewarding venture, but it requires careful planning and execution. From identifying your niche to developing a menu and choosing a location, there are several critical steps to consider. This section provides a comprehensive guide for entrepreneurs looking to break into the fast casual market, focusing on the essential components to build a successful business.
Identifying Your Niche and Target Market
Before diving into the operational aspects, it’s essential to define your restaurant’s concept and target audience. Here’s how to get started:
- Research the market:
- Analyze current fast casual trends to identify gaps or underserved niches.
- Consider popular concepts like health-focused menus, ethnic cuisine, or plant-based offerings.
- Understand your customer base:
- Are you targeting busy professionals, health-conscious millennials, or families seeking quality meals?
- Develop customer personas to refine your offerings based on demographics, lifestyle, and dining habits.
Identifying a niche that resonates with your target audience helps set your restaurant apart in a crowded market.
Developing a Menu that Stands Out
Your menu is the heart of your fast casual restaurant, and it needs to offer both quality and uniqueness. Consider the following:
- Simplicity and efficiency:
- Design a streamlined menu with a focus on high-quality, fresh ingredients.
- Limit the number of menu items to ensure fast preparation times and reduce kitchen complexity.
- Customization options:
- Allow customers to personalize their meals with a “build-your-own” concept (e.g., bowls, salads, or sandwiches).
- Offer a variety of proteins, grains, and vegetables to cater to dietary preferences like vegan, gluten-free, or keto.
- Signature dishes:
- Create a few standout menu items that define your brand and keep customers coming back.
A well-planned menu that balances variety with simplicity is key to ensuring operational efficiency while attracting diverse customer preferences.
Choosing the Right Location for a Fast Casual Concept
Location is crucial to the success of your fast casual restaurant. Here’s what to consider:
- High foot traffic areas:
- Look for locations near busy office buildings, shopping centers, or universities where people need quick meal options.
- Proximity to your target market:
- Ensure the location aligns with your customer demographics—whether it’s in a health-conscious urban neighborhood or a suburban family area.
- Accessibility:
- Easy access to parking, public transport, and delivery services is essential for maximizing customer convenience.
The right location can significantly impact your restaurant’s visibility and foot traffic, making it a key decision in your business plan.
Cost Breakdown: Initial Investments and Ongoing Expenses
Starting a fast casual restaurant requires a clear understanding of both initial and ongoing costs. Here’s a breakdown:
- Initial investments:
- Lease or property purchase: Location costs will vary significantly depending on the area.
- Renovation and equipment: You’ll need to invest in kitchen appliances, furniture, point-of-sale systems, and interior design to fit your concept.
- Permits and licenses: Ensure you budget for all required permits, such as health and safety certifications, business licenses, and food handling permits.
- Ongoing expenses:
- Staff salaries: Although labor costs are lower than full-service restaurants, you’ll still need to budget for kitchen staff and counter service employees.
- Food and supplies: Regular inventory purchases, including fresh ingredients, packaging, and cleaning supplies.
- Marketing and advertising: Allocating a budget for both online and offline marketing to promote your restaurant.
By thoroughly understanding your startup and operational costs, you’ll be better equipped to manage your finances and maintain profitability.
Marketing Strategies to Attract the Fast Casual Customer
Effective marketing is essential for generating buzz and attracting customers to your fast casual restaurant. Consider these strategies:
- Social Media Campaigns:
- Leverage platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok to showcase your dishes, behind-the-scenes content, and special promotions.
- Use location-based hashtags to target potential customers in your area.
- Loyalty Programs and Apps:
- Offer incentives like points for repeat visits or discounts on future purchases through a loyalty app.
- Encourage customers to sign up for newsletters or loyalty programs to receive exclusive offers.
- Collaborations with Local Influencers:
- Partner with food bloggers or local influencers to promote your restaurant through sponsored posts or events.
- Invite them to review your menu or attend a special launch to generate word-of-mouth buzz.
A multi-channel marketing approach can help build your restaurant’s brand and bring in new customers, particularly in the fast-paced fast casual market.
Starting a fast casual restaurant involves balancing creativity with practicality. By identifying a unique niche, developing a standout menu, and securing a prime location, you’ll be well on your way to launching a successful business. Additionally, a solid financial plan and effective marketing strategies will ensure your fast casual restaurant gains traction and grows in an increasingly competitive industry.
Examples of Successful Fast Casual Restaurants
The fast casual dining industry is filled with standout brands that have successfully combined convenience, quality, and innovation to attract loyal customers. These restaurants have pioneered new approaches to food, service, and customer engagement, setting benchmarks for others to follow. In this section, we will explore some of the most successful fast casual restaurant chains around the world, examining their unique business models and what has made them thrive in this competitive industry.
Case Study: Chipotle’s Focus on Transparency and Customization
Chipotle Mexican Grill is often regarded as one of the pioneers of the fast casual movement. Key factors behind its success include:
- Transparency in sourcing:
- Chipotle emphasizes using fresh, sustainably sourced ingredients, including non-GMO and organic options.
- The company has long focused on ethical farming practices, setting it apart from traditional fast food chains.
- Customization at the core:
- Chipotle’s “build-your-own” model allows customers to personalize their meals, from burritos to bowls, selecting their favorite ingredients.
- This customization has led to a strong customer loyalty, as diners appreciate the ability to create meals that fit their dietary preferences.
- Simplicity with flavor:
- Despite a relatively simple menu, Chipotle excels by offering flavorful, high-quality dishes that keep customers coming back.
Chipotle’s success lies in its ability to deliver fresh, customized meals at an affordable price, while maintaining a commitment to ethical sourcing.
How Panera Bread Revolutionized Fast Casual with Fresh Bread
Panera Bread has distinguished itself by emphasizing artisanal bread and café-style dining. Here’s what has contributed to its ongoing success:
- Focus on freshly baked goods:
- Panera is known for baking its bread fresh daily, which serves as the foundation for many of its popular menu items, such as sandwiches, soups, and salads.
- This commitment to fresh, high-quality ingredients has helped Panera create a loyal customer base.
- Café-style atmosphere:
- Panera offers a cozy, welcoming environment that encourages customers to sit and enjoy their meals, while still providing the convenience of fast casual service.
- Many locations include free Wi-Fi, which has attracted a steady flow of students, freelancers, and professionals.
- Health-conscious options:
- Panera has continuously innovated its menu to include healthier options, such as vegetarian, gluten-free, and low-calorie dishes.
- It was also one of the first major chains to post calorie counts on its menu, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Panera’s blend of quality ingredients, warm atmosphere, and nutritional transparency has helped it become one of the most recognizable names in fast casual dining.
The Role of Technology in Sweetgreen’s Success
Sweetgreen has set itself apart by embracing technology and sustainability to attract health-conscious diners. Here’s how it became a fast casual success:
- Tech-forward approach:
- Sweetgreen has integrated technology into its operations, offering a seamless mobile app experience for ordering and delivery.
- The brand’s app allows customers to customize their orders, track nutrition information, and earn rewards, creating a tech-savvy customer experience.
- Sustainability at the forefront:
- Sweetgreen focuses on locally sourced, organic ingredients and is committed to reducing its environmental footprint through sustainable packaging and food waste reduction initiatives.
- The brand also emphasizes seasonal menus, ensuring freshness while supporting local farmers.
- Modern, minimalist branding:
- Sweetgreen’s clean, minimalist branding and trendy interiors appeal to a younger, urban crowd that values aesthetics and experience in addition to good food.
Sweetgreen’s blend of technology, sustainability, and health-focused menus has helped it build a strong reputation in the fast casual market, especially among millennials and Gen Z.
LEON’s Mission to Serve Healthy Fast Food
LEON, a UK-based chain, has redefined fast food with its commitment to healthy, flavorful meals. Here’s what makes LEON stand out:
- Healthy “fast food” concept:
- LEON’s tagline, “Naturally Fast Food,” reflects its commitment to offering nutritious, Mediterranean-inspired dishes, such as grilled chicken, falafel, and quinoa salads.
- The brand focuses on using whole foods, free from artificial ingredients, preservatives, and refined sugars.
- Sustainability initiatives:
- LEON takes a strong stance on environmental responsibility, from sourcing sustainable ingredients to using compostable packaging.
- The company has also made strides in reducing its carbon footprint by offering more plant-based options.
- Inclusive menu offerings:
- LEON caters to a wide range of dietary preferences, with options for vegans, vegetarians, and those on gluten-free or dairy-free diets.
- This inclusivity has helped the brand build a diverse and loyal customer base.
LEON’s innovative approach to serving healthy, ethically sourced meals at fast food speed has made it a standout in the European fast casual scene.
These successful fast casual brands each bring something unique to the table, whether it’s a commitment to sustainability, technological innovation, or a focus on health-conscious dining. By staying true to their core values and continuously evolving to meet consumer demands, these restaurants have set benchmarks for success in the fast casual industry.
Future of Fast Casual Dining
The fast casual dining industry is rapidly evolving as it adapts to emerging consumer trends, technological advancements, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. As this sector continues to grow, restaurants will need to innovate in areas like menu offerings, customer experience, and environmental responsibility to stay ahead of the competition. In this section, we’ll explore key trends that are shaping the future of fast casual dining and how businesses can prepare for these changes.
Predicted Growth for Fast Casual Post-2024
The fast casual sector is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by consumer demand for high-quality, convenient dining options. Key factors fueling this growth include:
- Changing consumer habits:
- As more people prioritize healthier, fresher food, fast casual restaurants are well-positioned to capture this audience.
- The increasing demand for meal customization and dietary flexibility, such as plant-based, gluten-free, and keto options, will keep this sector appealing to diverse customer groups.
- Shift away from traditional fast food:
- Consumers are becoming more conscious about what they eat, leading to a decline in traditional fast food in favor of fast casual alternatives that offer better quality and healthier choices.
- International expansion:
- As fast casual dining proves successful in markets like North America and Europe, more brands will seek to expand globally, tapping into growing middle-class markets in regions like Asia, Latin America, and Africa.
This growth presents significant opportunities for both established brands and new entrants in the fast casual space, but they will need to stay ahead of emerging trends to maintain their competitive edge.
Sustainability Trends in Fast Casual Restaurants
Sustainability will continue to be a key driver of success in the fast casual industry as consumers increasingly demand environmentally responsible dining options. Key sustainability trends include:
- Plant-based and alternative proteins:
- The shift toward plant-based diets is expected to accelerate, with more restaurants incorporating options like Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods, and other plant-based proteins.
- These innovations will cater to a broader customer base, including vegetarians, vegans, and flexitarians who want to reduce their meat consumption.
- Eco-friendly practices:
- Fast casual restaurants will continue to adopt sustainable practices, such as reducing plastic use, implementing compostable packaging, and sourcing locally grown ingredients.
- Many brands are also investing in reducing food waste by implementing better inventory management systems and donating excess food.
- Carbon-neutral initiatives:
- Some fast casual chains are exploring ways to become carbon-neutral, from reducing emissions in their supply chains to incorporating renewable energy in their operations.
Embracing sustainability will not only help fast casual restaurants meet consumer demand but also differentiate them in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
How Tech Innovation Will Shape the Fast Casual Experience
Technology is transforming how fast casual restaurants operate and interact with customers, and this trend is set to continue. Here are some of the key tech innovations reshaping the industry:
- Self-Ordering Kiosks:
- Self-ordering kiosks are becoming more prevalent in fast casual restaurants, allowing customers to place and customize their orders directly, reducing wait times and enhancing accuracy.
- These kiosks also provide opportunities for upselling and promoting special offers, contributing to increased revenue.
- Digital Menus and QR Code Integration:
- The rise of digital menus and QR code ordering systems has streamlined the customer experience, allowing diners to order from their smartphones without needing to wait in line.
- These technologies have proven especially valuable during the COVID-19 pandemic, and their convenience is expected to make them a permanent fixture in the industry.
- Data-driven personalization:
- Many fast casual restaurants are using customer data to personalize the dining experience. Apps that track order history can offer customized recommendations, loyalty rewards, and personalized promotions to keep customers engaged and returning.
By embracing technology, fast casual restaurants can enhance the overall customer experience, improve operational efficiency, and remain competitive in a digital-first world.
The Impact of Changing Consumer Preferences
As consumer preferences evolve, fast casual restaurants must continuously adapt to stay relevant. Some of the emerging consumer trends include:
- Health and wellness:
- Health-conscious dining will remain a priority for consumers, driving demand for meals that focus on fresh, nutrient-dense ingredients. Fast casual brands that emphasize transparency, clean eating, and balanced nutrition will continue to thrive.
- Ethical and social responsibility:
- Consumers are increasingly drawn to brands that demonstrate ethical values, such as supporting fair trade practices, using sustainable ingredients, and prioritizing employee welfare.
- Restaurants that take a stand on social issues or contribute to local communities are likely to build stronger, more loyal customer bases.
- Experience-driven dining:
- As diners seek more than just a meal, fast casual restaurants will need to focus on creating a memorable, engaging dining experience. From unique interior designs to interactive food preparation, providing an experience that goes beyond the food will become a key differentiator.
Adapting to these consumer preferences will be crucial for fast casual restaurants aiming to maintain their relevance in the competitive dining landscape.
The future of fast casual dining is bright, with growth opportunities fueled by sustainability, technological innovation, and shifting consumer preferences. Restaurants that embrace these trends and stay ahead of industry changes will continue to thrive in the ever-evolving food service market.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Erkin Coban
Your Customers Deserve The Best
And we got Menuviel for them.
The fastest and easy-to-use online QR menu with 12+ unique features. Choose Menuviel and elevate your service quality to the next level.
Use free for the first 30 days.

In This Article

Free AI Tools for Restaurants
TRY NOW ➜
Lightning-fast loading pages and images
Your menu loads instantly with optimized images—no waiting, just a smooth browsing experience.







